MARKETING & SUSTAINABILITY
Product Innovation for Sustainability
Marketing professionals are uniquely positioned to influence what products and services are offered and how they are made. To protect our atmosphere, oceans and communities, we are certainly going to need more and different kinds of products in every industry. Consider the challenge (as presented by the World Business Council for Sustainable Development):
-
- a global population of 9 billion expected by 2050
- the global middle class tripling by 2030
- natural resource consumption expected to rise to 170% of the Earth’s bio-capacity by 2040
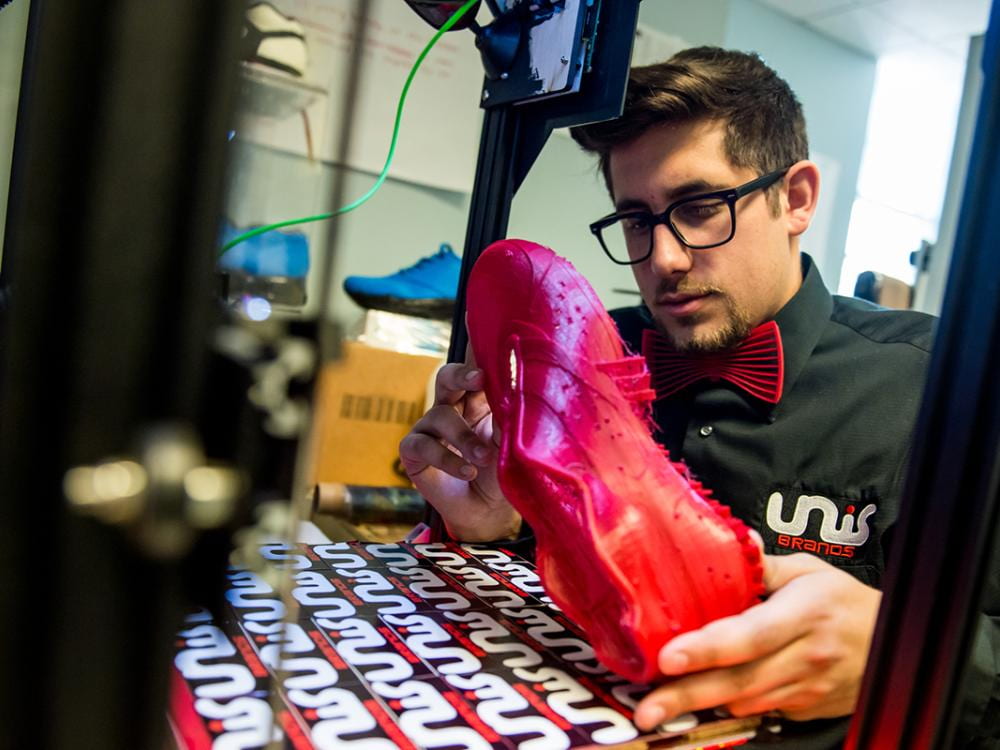
Marketers may initially help companies develop and sell products that do less harm (to people and the environment). Leading companies however innovate products and services that maximize benefits to people and planet. Unisbrands (pictured right), for example, plays a part in cleaning up oceans as they use ocean plastic as an input into their 3-D printing process.
Finally, adding sustainable products can happen organically or through acquisition. Organic growth into sustainable products often involves a careful choice of a product category that can be used to prototype ideas (e.g. Clorox creates Green Works). Acquisitions have abounded in this space as larger companies have purchased smaller sustainable brands.
Penn State masters in accounting student Nicholas Unis founded Unisbrands which 3-D prints shoes with polymers from plastic waste-streams. The shoes themselves are recyclable into new shoes.

Small Innovations: Product and Packaging Changes That Can Make a Difference
Product innovation for sustainability can be a highly complex strategic area for a business.
On the simpler side are tweaks to existing products. Though not true “innovation” such changes certainly can add up and make a difference. Changes can be in the following product attributes areas:
-
- durability
- energy efficiency
- sustainably and ethically sourced materials
- low/no toxicity
- clean energy/fuels
- repairability
- recyclability (of product and packaging)
- returnable for remanufacturing
Of course, these attributes must be cost-effective, meet or exceed customer expectations, and be built on solid technical analysis.
Big Innovations: Changing Product-Customer Systems for Sustainability
Beyond the small tweaks, are whole system changes that involve process improvements and innovations up and down value chains, new ways of communicating with and engaging customers in circular systems, and new organizational structures and compensation processes for sales people and account managers who may not be selling products but leases and service contracts.
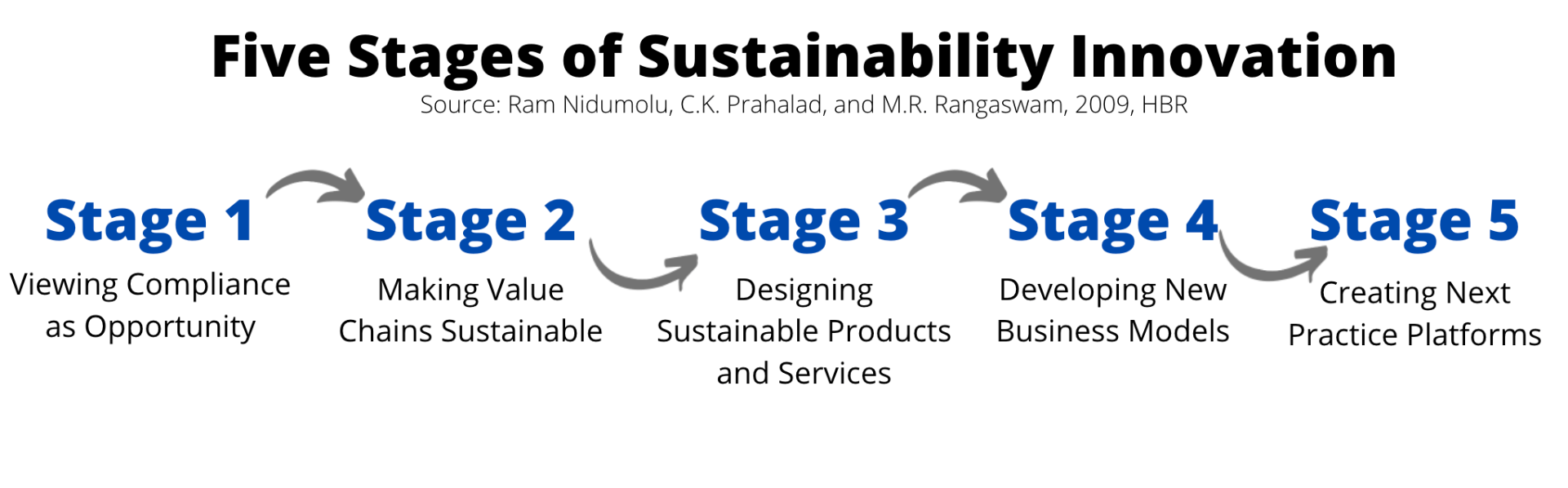
Here we take our inspiration from the famous 2009 Harvard Business Review article “Why Sustainability Is Now the Key Driver of Innovation“
Central challenge: ensure that compliance becomes an opportunity for innovation.
Innovation opportunity
- using compliance to induce the company and its partners to experiment with sustainable technologies, materials, and processes
Central challenge: increase efficiencies throughout the supply chain.
Innovation opportunities
- developing sustainable sources of raw materials and components.
- increasing the use of clean energy sources
- finding innovative uses for returned products
Central challenge: develop sustainable offerings or redesign existing ones to become sustainable
Innovation opportunities
- applying techniques such as biomimicry in product development
- developing sustainable packaging
Central challenge: define novel ways of delivering and capturing value, which will change the basis of competition
Innovation opportunities
- developing new delivery technologies that change value chain relationships in significant ways
- creating monetization models that relate to Services rather than products
- devising business models that combined digital and physical infrastructures
Central challenge: to question through the sustainability lens the dominant logic behind business today
Innovation opportunities
- building business platforms that will enable customers and suppliers to manage energy and radically different ways
- developing products that won’t need water in category is traditionally associated with it, such as cleaning products
- designing technologies that will allow Industries to use the energy produced as a byproduct
Learn about more sustainability concepts within this major.
ADVANCE YOUR KNOWLEDGE OF SUSTAINABLE MARKETING
Learn what sustainable marketing is all about and its importance
Learn the important things to know in this field
Learn how sustainability fits into your courses
Learn how sustainability relates to your career